As digital services continue to expand, the way data is processed and delivered is changing. Applications that rely on real-time analytics, connected devices, streaming, and artificial intelligence require faster response times than traditional centralized data centers can always provide. This shift has led to the growth of edge data centers.
Edge data centers are becoming a critical part of modern infrastructure strategies, particularly for organizations that need low latency, local data processing, and distributed computing environments. Understanding what an edge data center is and how it works can help organizations plan infrastructure that supports performance, scalability, and reliability.
What Does “Edge” Really Mean?
In technology, the “edge” refers to locations that are close to the users, devices, or systems that generate data. Rather than sending every bit of data back to a centralized facility that could be hundreds or thousands of miles away, edge computing processes data locally or regionally.
An edge data center is simply a data center that is positioned in those local or regional environments.
It is not defined by size or capacity. Instead, its value comes from location and purpose, processing data near where it matters most so systems can respond quickly and reliably.
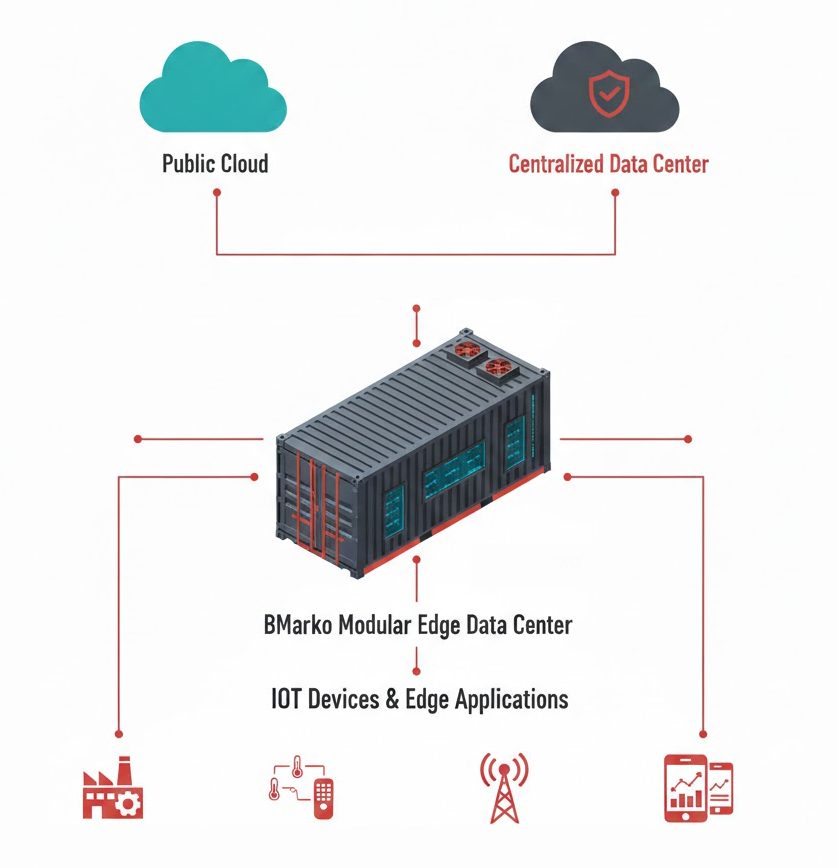
How Edge Data Centers Differ From Traditional Data Centers
Traditional data centers are centralized facilities designed to support broad computing workloads across an entire enterprise or region. They are often large, built with redundant infrastructure, and optimized for maximum reliability and capacity.
Edge data centers, on the other hand, are typically:
- Smaller in scale
- Closer to end users or connected devices
- Designed to process data with minimal delay
- More distributed across geographic areas
The difference boils down to where and how data is processed:
- In a traditional model, data travels to a central facility for computation, then back to the user device or endpoint.
- In an edge model, data is handled locally or regionally, reducing round-trip time and lowering latency.
This shift is especially important for applications that need rapid responses, such as autonomous systems, video streaming, gaming, industrial automation, and Internet of Things (IoT) networks.
Why Edge Data Centers Matter

Reduced Latency
Latency is the delay between sending a request and receiving a response. When data is processed far from the source, that delay can add up. Edge data centers reduce latency by moving compute capacity closer to end users, which improves responsiveness for time-sensitive applications.

Improved Reliability
If a centralized data center becomes unreachable due to network issues, local processing at the edge can keep critical systems running. This is especially important for operations that cannot afford interruptions, such as medical monitoring or industrial automation.

Lower Bandwidth Costs
Instead of sending all data to a central facility and back, edge data centers can filter and process data locally. Only the information that truly needs long-term storage or deep analysis gets transmitted over wide area networks, reducing bandwidth usage and cost.

Support for IoT and Mobile Growth
The number of connected devices is growing rapidly. Smart sensors, mobile devices, autonomous vehicles, and industrial systems generate enormous amounts of data. Processing more of that data at the edge keeps networks from becoming bottlenecked and ensures performance remains stable.
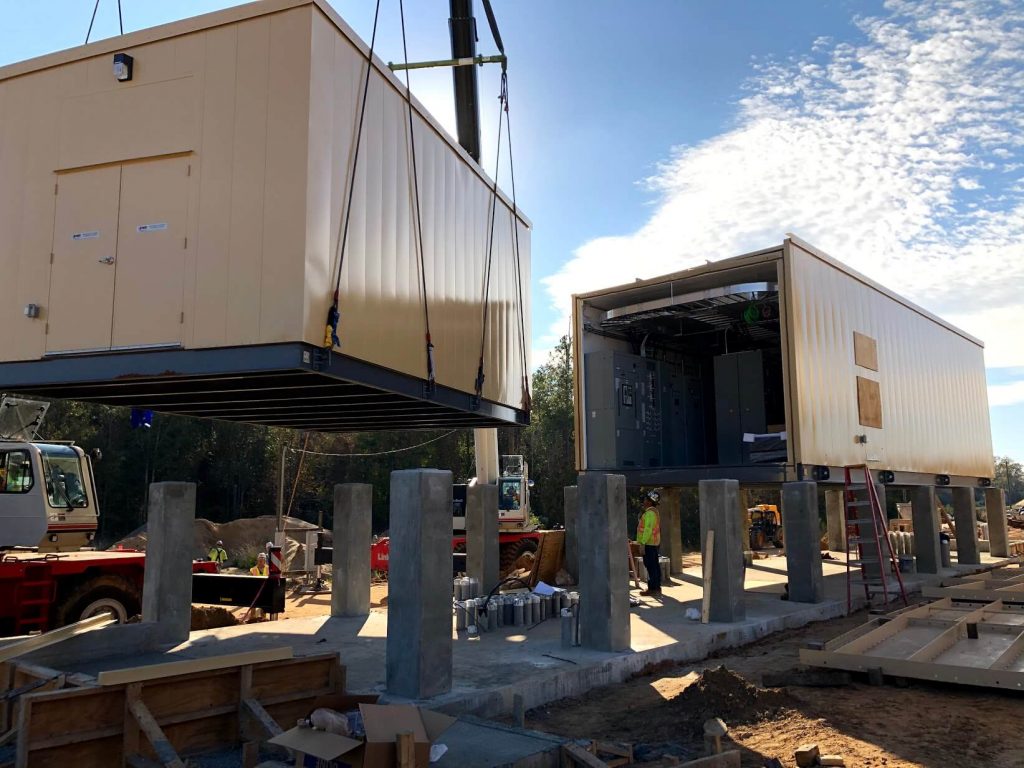

How Edge Data Centers Are Built
Edge data centers can be custom-built on-site, integrated into existing buildings, or created using modular and prefabricated designs. Many organizations prefer modular deployments because they can be built faster, standardized, and expanded over time as demand grows.
Because edge locations vary widely, from urban centers to remote rural corridors, flexible approaches to infrastructure design are essential to meet capacity, environmental, and budget requirements.
Where BMarko Structures Fits In: Prefabricated Modular Solutions
The physical infrastructure supporting edge data centers must be reliable, secure, and designed for long operational life. That is where BMarko Structures plays a central role.
BMarko is not a full-stack data center designer or systems integrator. Instead, BMarko specializes in structural enclosures and build-ready infrastructure that support edge and modular data center deployments.
That includes:
Engineering and building durable, code-compliant enclosures for edge facilities
Working with site constraints to deliver structures that are fit for purpose
Coordinating with trusted partners who handle power, cooling, and IT systems
Providing guidance and support through planning and construction phases
By focusing on the physical structure, BMarko helps organizations ensure the foundation of their edge data center is built right, so the rest of the system can perform as expected.
Whether an organization needs a standalone edge facility, a modular addition near an enterprise site, or a hybrid deployment, BMarko brings deep experience in delivering purpose-built enclosures and coordinating with broader infrastructure teams.
Ready to Learn More About Edge Data Centers?
Edge data centers are a fundamental part of modern infrastructure strategies. They bring computing resources closer to where data is generated and consumed, improving performance, reliability, and efficiency for real-time applications.
By understanding what edge data centers are, how they operate, and the role they play alongside traditional data centers, organizations can make smarter decisions about where and how to deploy infrastructure.
If you are exploring an edge data center strategy or evaluating what an edge deployment could look like in your environment, connect with BMarko Structures to talk through your goals and next steps.
Contact Us
"*" indicates required fields
- 134 Long Rd Suite 200, Williamston, SC 29605
- (678) 666-3688
- [email protected]
